In this highly networked business world, there may be some dichotomous perceptions in the minds of C-suite such as:
Why does one executive outperform his/her colleagues?
What is the effect of training and development programs on company’s overall performance?
What will be the minimum duration for new personnel to get acquainted with the system and start showing results?
Why do some Managers flourish and others perish?
If one stop solution is surfed to all such interrogations, then they have to hit the Big Data and derive logical analysis. In fact, the companies are not in dearth of data, they do have abundance of data to critically analyze. But, the million dollar question is how to use it logically for getting required analysis. If the concern is to logically analyze data than just compiling them, then HR Analytics come in handy in all dimensions.
Exhibit 1- The stages of HR Analytics
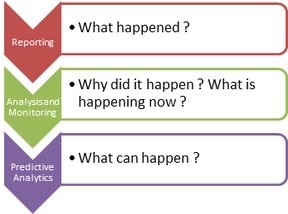
Exhibit 2- HR Analytics beyond HR Reporting
Although, HR reporting plays a significant role in people management, it should not be confused with HR analytics as it has got its own impact and implications.
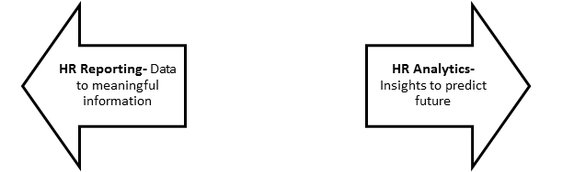
Exhibit 3- Applications of HR Analytics
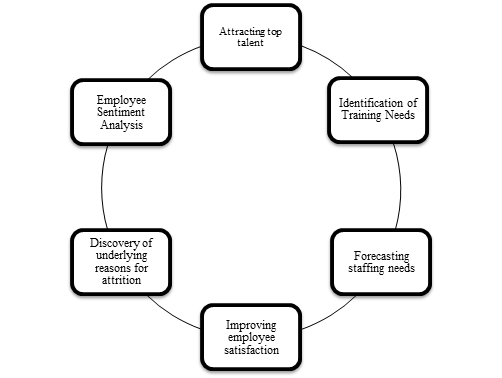
Accoring to Dr. Salvatore Falletta, Managing Director for the Organizational Intelligence Institute
“HR analytics encompasses the full range of HR research and analytics related practices including workforce surveys and assessments, 360° feedback, metrics and indicators, benchmarking, human capital research, employee and talent profiling, talent forecasting, learning evaluation, and more.”
Exhibit 4 – 4 As of HR Analytics
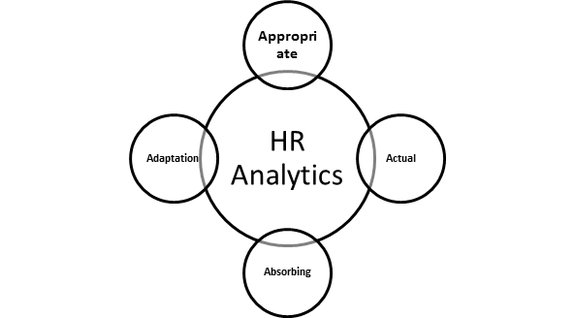
Appropriate: In order to get meaningful results, HR analysts need to relate pertinent data to the business problem rather than using a redundant amount of information.
Actual: In HR Analytics, in addition to the quality of data, Managers must be appraised about the trustworthiness of Human Resource metrics.
Absorbing: HR department should not get carried away with disseminating raw numbers and anticipating the receiver to ascertain the exact interpretations. HR Analysts have to know their spectators, construct related storylines and inscribe conclusions that pool together the fundamental details.
Adaptation: In the long run, meaningful analytics have to transform a Manager’s perception and attitude. With the help of HR Analytics data, Managers should be able to bring alteration in their pattern of thinking and create swift and logical decisions.
Transmitting HR Data into Insight
Professional Human Resources Analytics system enables organizations to effectively accomplish and advance performance by:
Optimizing Talent: To improve overall cost-effectiveness through active HR cost control measures is the major objective of optimizing talent. In fact, executives can appreciate how to optimize the talent to make sure that reasonable distribution of service while retaining the lowest but efficient employees. There is also possibility of understanding the effect of paying overtime work versus staffing new employees on overall productivity.
HR Insight: Generating and disseminating HR Managers reliable and cohesive talent insight to efficiently manage employees’ performance and competencies. HR and top file and rank can get clarity into High, Slow and Low performing talents, to develop and retain key talents.
HR Causal Effect: Delivering the ability to correlate HR information with overall functioning processes to better apprehend the causal effect of HR investment on results in congruence to organizational objectives.
Uses of HR Analytics- Data Execution
Google has implemented HR Analytics in different functions of their respective HR department as mentioned below.
Company Name: Google
HR Function: Personnel Recruitment
Execution: Google applies its proprietary predictive modeling to the field of recruitment as well. They have learned not to rely on traditional performance indicators like school or GPA, which prove to not have much predictive value. Instead they use five key, measurable attributes that correlate with successful hires: coding ability, cognitive skills, leadership, humility & ownership. (Friedman 2014)
Article by: L. Gandhi, M.A., M.B.A., M.Phil., UGC-NET (Ph.D), Asst. Professor- OB/HRM
Mohamed Minhaj, MCA, M.Phil (Ph.D), Associate Professor – Systems
To stay connected with SDMIMD, click here.
